What is Edge Computing and How It is More Effective than Cloud Computing?
Posted by. Disrupt Tech. March 22, 2022
Edge computing is the new paradigm in the world of the internet and computing. It is getting so popular that the global market share is expected to grow by $205.6 billion at the end of 2024. So what makes edge computing so popular than cloud computing?
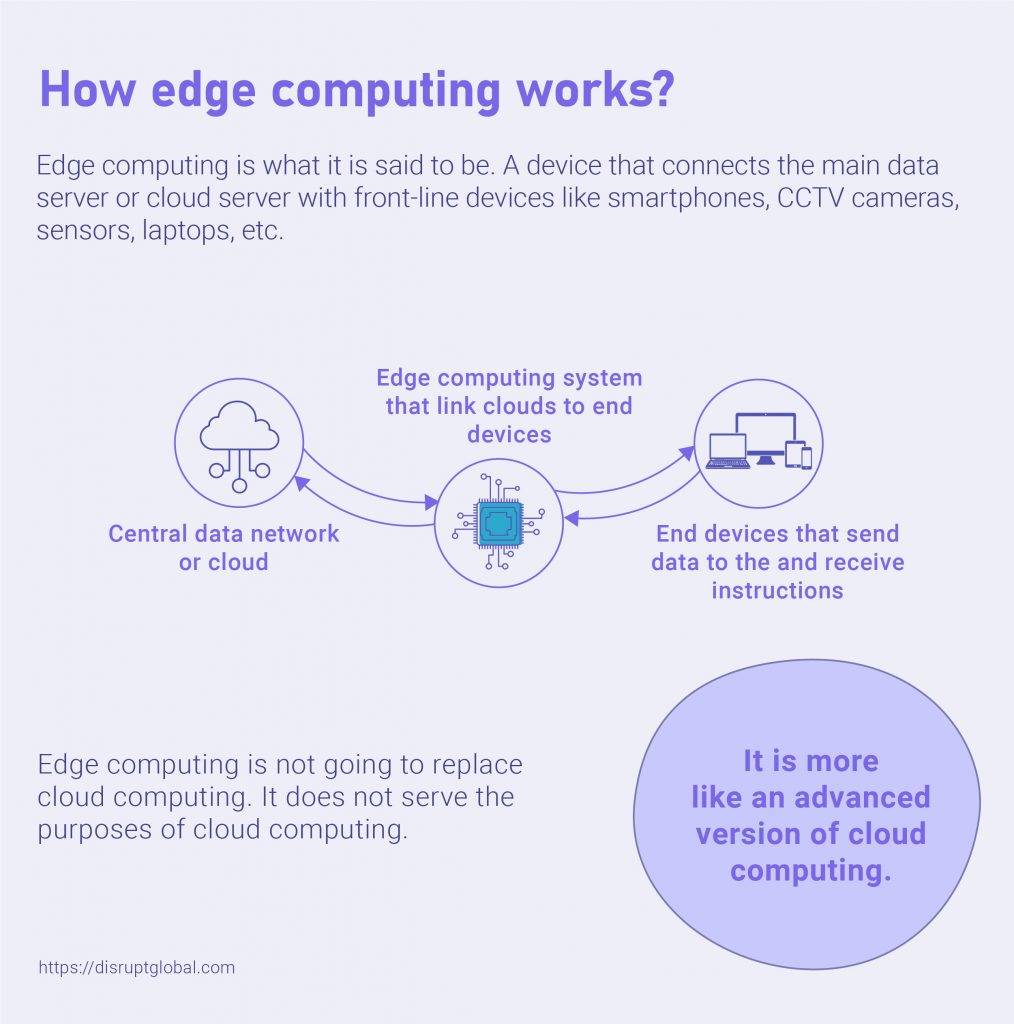
Let’s clear one thing here first. Edge computing is not going to replace cloud computing. It does not serve the purposes of cloud computing. It is more like an advanced version of cloud computing.
Edge computing is what it is said to be. A device that connects the main data server or cloud server with front-line devices like smartphones, CCTV cameras, sensors, laptops, etc.
Let’s try to think in this way. A fire broke into someone’s house. If there is no fire alarm and sprinkler system, things may go bad. If emergency actions are not taken, this will get bigger. It will take the fire department a couple of minutes to come into action.
But if there was an integrated fire alarm and sprinkler system, the problem would have been solved almost immediately.
Here the fire alarm and sprinkler system work like an edge technology.
Most of the devices are connected to a central data system or cloud system. The cloud network lets you not just save data but run apps on your devices from a remote server. The devices receive instructions from the cloud and send the feedback data to the cloud.
But due to the explosion of IoT, this model has many shortcomings. Modern IoT devices gather so much data that the volume needs larger and more expensive connections to the cloud. This also requires a faster data transferring system which the cloud system is unable to provide.
For example, sensors in vales find a strong and dangerous pressure in the pipes in an industrial factory. This needs to be shut down immediately. The main server which the process shuts down may be at a distance. It will take a few moments for the server to send the automated shutdown sequence. This may lead to a huge explosion and cause serious damage to property and people.
But if processing power is placed at the sensors in vales, the latency will be reduced. This will save damage to property and save lives.
By now you understand what is edge computing. Let’s explore how edge computing is effective than cloud computing in some areas.
Increase the Performance
Edge computing collects data from end devices to send to the cloud. It also performs tasks like processing, analyzing, and performing necessary actions on the data locally. Few processes take milliseconds to complete. This is why edge computing has become critical in optimizing data, regardless of the operations.
Transferring tons of data in real-time and at a low cost can be difficult. Because of modern technology, data is massive in amount. There are many cases where processing units are far away from industrial sites. Sending this huge amount of data takes lots of time. This issue can be solved by infusing AI into network edge devices.
As said earlier, if such tasks are done by the cloud, it can be devastating. Cloud takes lots of time to respond and the transmission speed is not that up to the mark. Edge computing is faster, less expensive, and responds in milliseconds. It removes the middleman by bringing analytical capabilities closer to the machine.
Decrease the Operational Cost
Maintaining a cloud server is quite expensive. Connectivity, data transfer, bandwidth, and latency are very costly. It costs way more when clouds have to work directly with end devices.
On the other hand, edge computing requires less bandwidth and has lower latency. It perfectly removes the inefficiency of data transmitting. This makes the operational cost lesser than cloud servers.
Edge computing creates a valuable continuum from the device to the cloud, capable of handling the vast volumes of data generated. You don’t need to upload gigabytes of data to the cloud. This is why expensive bandwidth upgrades are no longer necessary.
It also analyzes sensitive IoT data in a private network, ensuring that sensitive data is protected. Edge computing is becoming increasingly popular among businesses:
» Predictive maintenance in high-tech industries e.g. Gas industry or the oil industry.
» Providing support to the remote working workforces.
» Autonomous vehicles.
» Smart streaming services.
» Retail and e-commerce optimization.
» Innovation in the healthcare industry.
‘Onion Skin’ Approach in Data transferring
The edge device could collect and analyze data from a set of IoT devices. Digital devices working in real-time produce lots of data. But the most amazing part is that it filters out data that is useless.
It can even see if something indicates an obvious problem. After directing an issue, it sends it down to the centralized cloud or another. If sending to the central server is not possible, it sends to a more powerful edge device closer to the core for examination.
For a better experience, ‘How edge computing is more effective than cloud computing’ is shown below:
Cloud Computing or Edge Computing or Both?
Both cloud computing and edge computing are beneficial. Now the question arises, which one should you use?
If you are wondering about which one to pick, here is the answer for you. It’s not an “either/or” situation when it comes to picking edge or cloud computing. Companies will need to make useful edge computing systems to maximize the use of IoT devices. As days go by, IoT devices will grow more pervasive and powerful.
Companies can mitigate their limitations by combining edge computing with centralized cloud computing (commonly known as fog computing). Many companies are doing so by co-locating their IT infrastructure with a data center.
In other words, tasks that need immediate attention and faster response should be processed by edge devices. And big data applications which require more analysis and machine learning should stay in the cloud. Companies need to define the fine line between cloud computing and edge computing for their success.